Bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of the soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Ultimate bearing capacity is the theoretical maximum pressure that can be supported without failure.
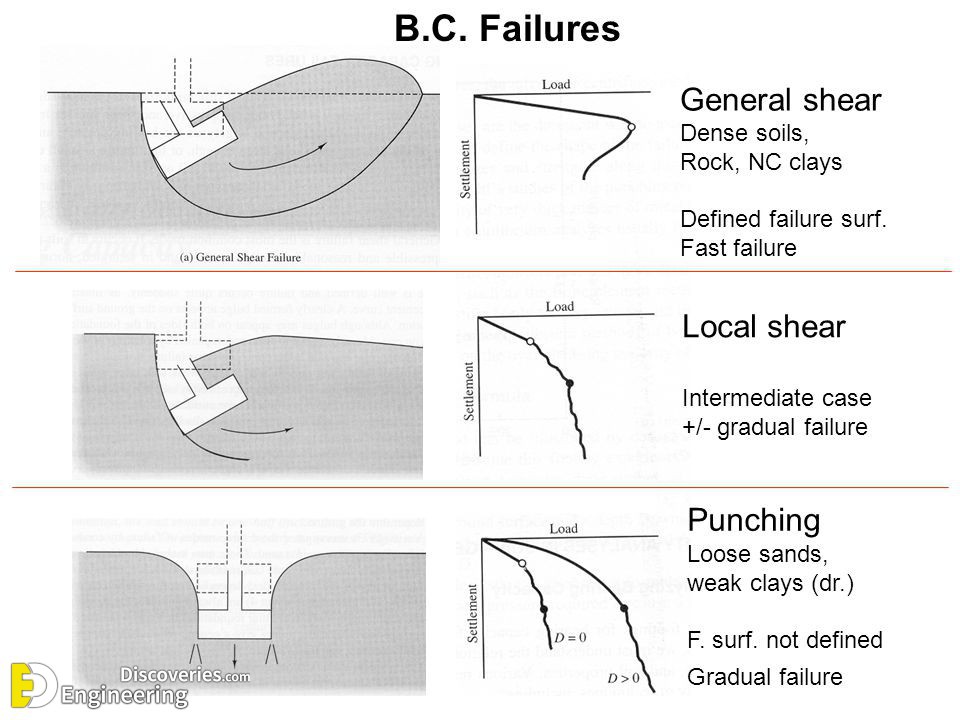
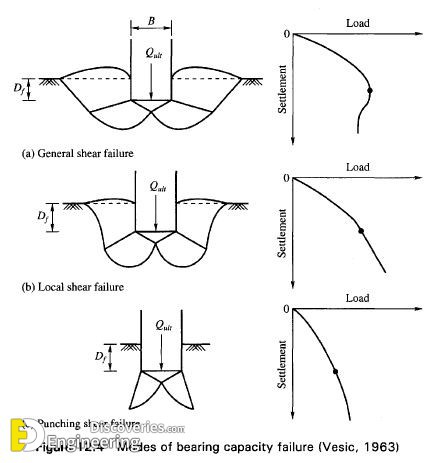
Allowable bearing capacity is the ultimate bearing capacity divided by a factor of safety. Sometimes, on soft soil sites, large settlements may occur under loaded foundations without actual shear failure occurring, in such cases, the allowable bearing capacity is based on the maximum allowable settlement. There are three modes of failure that limit bearing capacity: general shear failure, local shear failure, and punching shear failure.
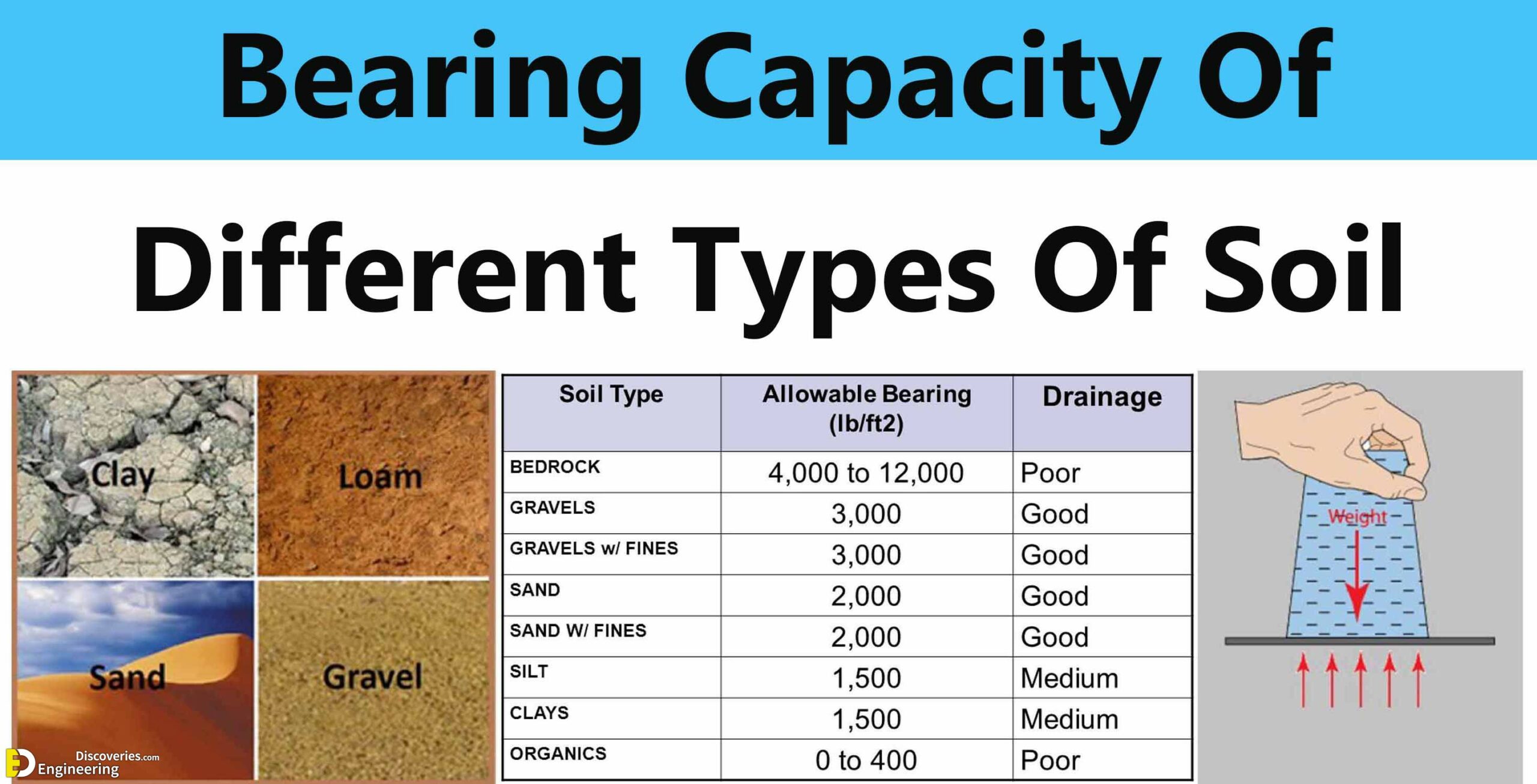
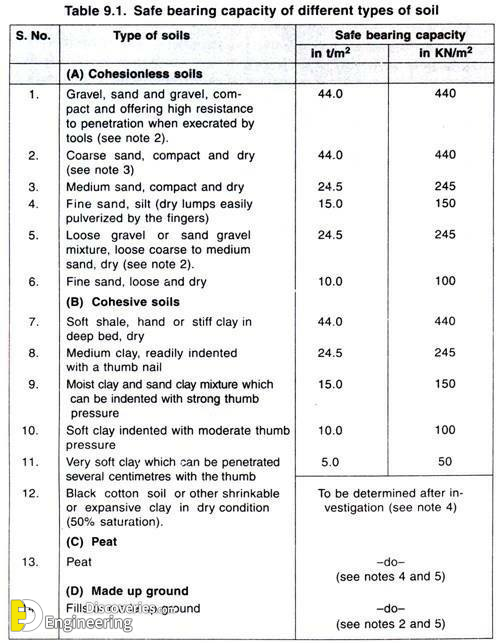
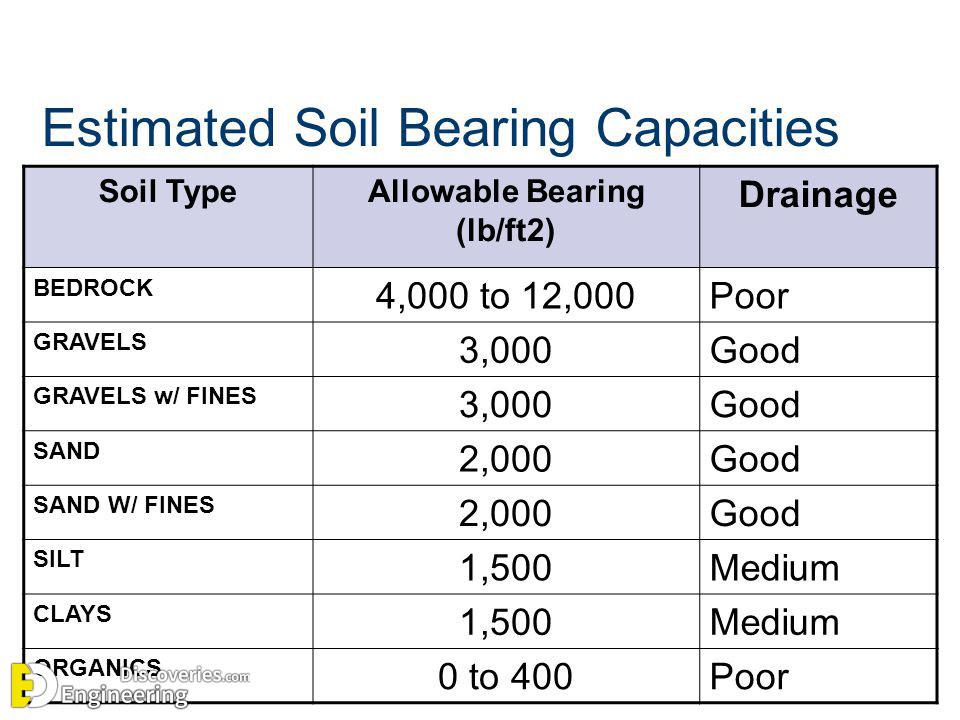
The following table shows the maximum bearing capacity values of different types of soils
|
Types of Soil |
Bearing Capacity (Kg/m2) |
Bearing Capacity (kN/m2) |
|
Soft, wet clay or muddy clay |
5000 |
50 |
|
Soft clay |
10000 |
100 |
|
Fine, loose, and dry sand |
10000 |
100 |
|
Black cotton soil |
15000 |
150 |
|
Moist clay and sand-clay Mixture |
15000 |
150 |
|
Loose gravel |
25000 |
250 |
|
Medium clay |
25000 |
250 |
|
Medium, compact and dry sand |
25000 |
250 |
|
Compact clay |
45000 |
450 |
|
Compact sand |
45000 |
450 |
|
Compact gravel |
45000 |
450 |
|
Soft rocks |
45000 |
450 |
|
Laminated rock such as sandstone & Limestone |
165000 |
1650 |
|
Hard rocks such as granite, diorite, trap |
330000 |
3300 |
Bearing capacity soil depends on the different soil when the soil condition is changed so the bearing capacity must be changed from the other types of soil. when we design any structure so, first of all, we have to check the bearing capacity of the soil by which we are designing our project.
Click Here To See (What Is Underpinning? Uses In Foundation Strengthening And Methods)