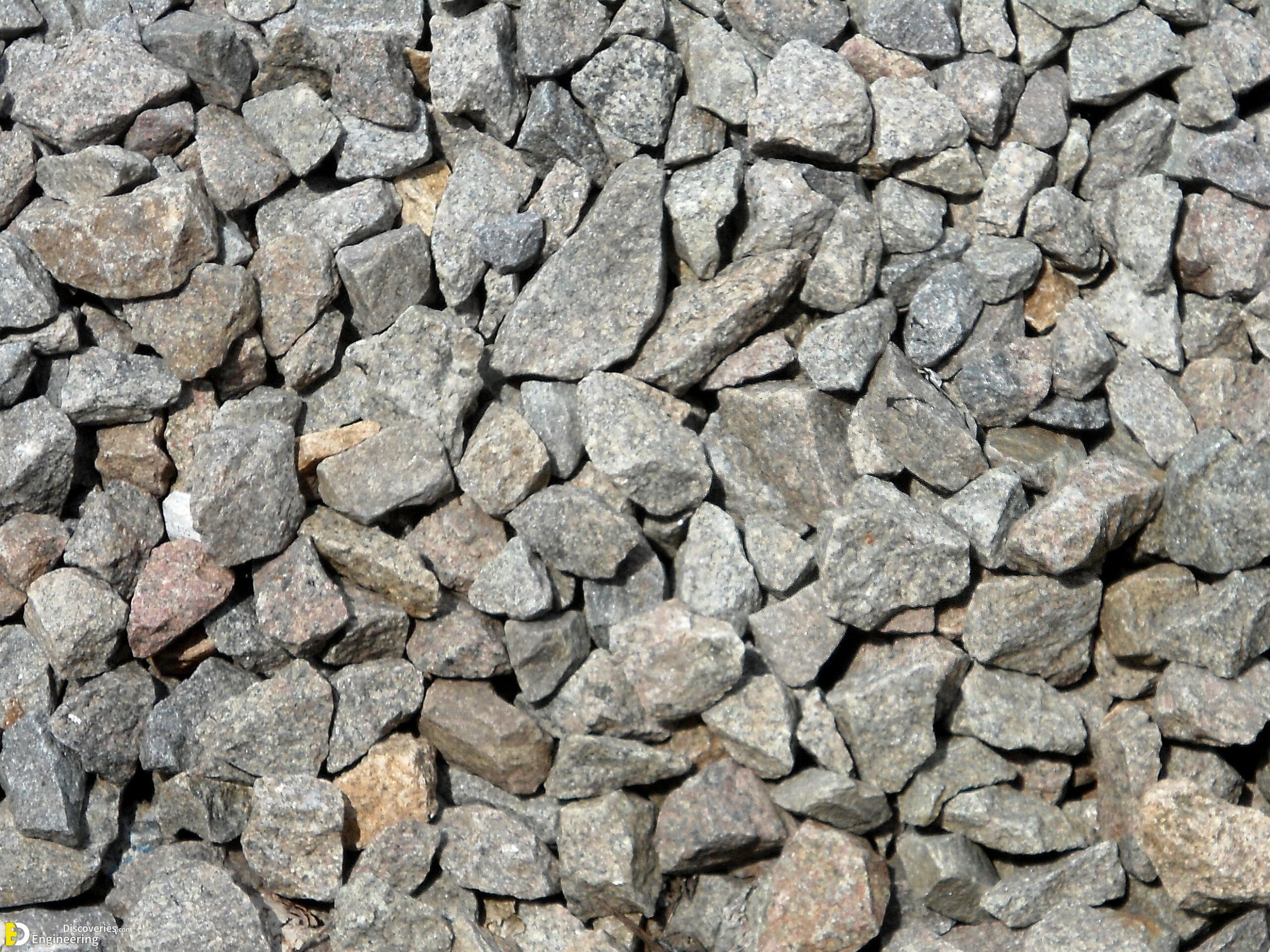
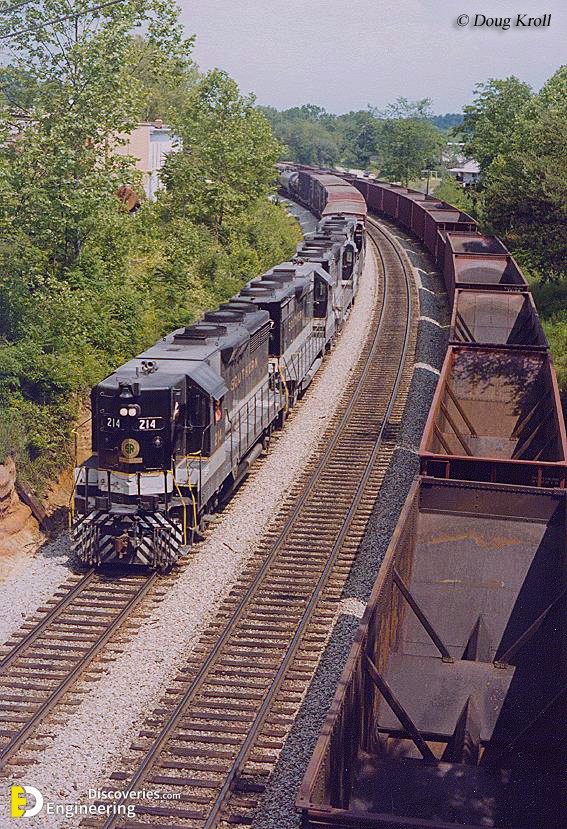
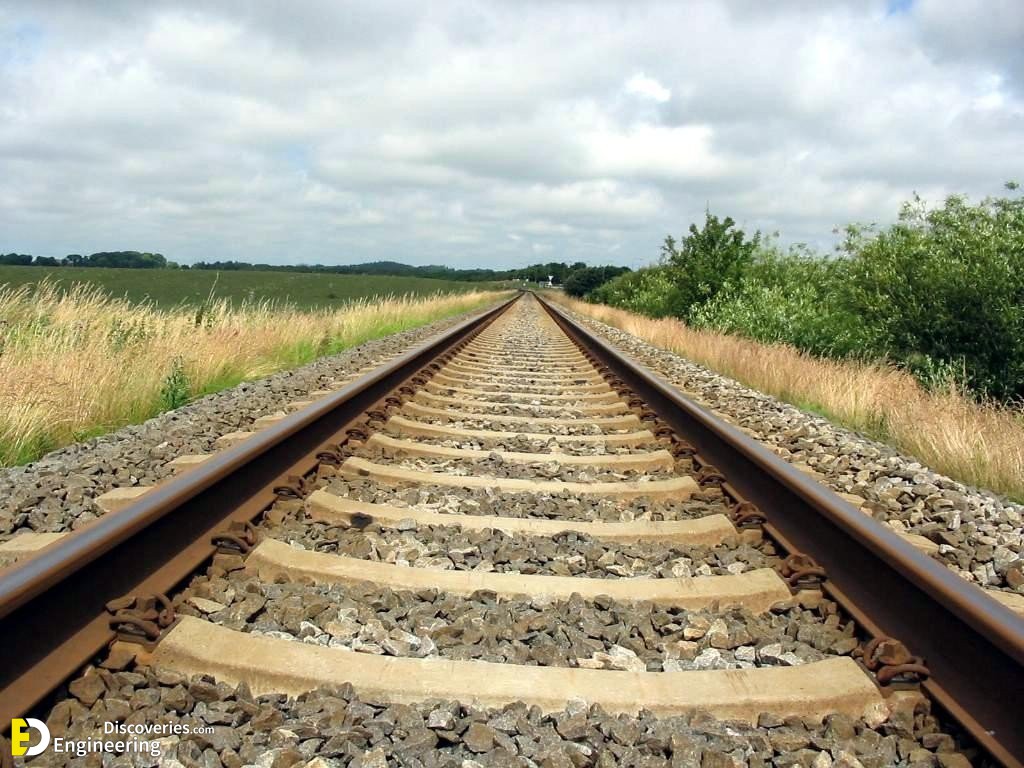
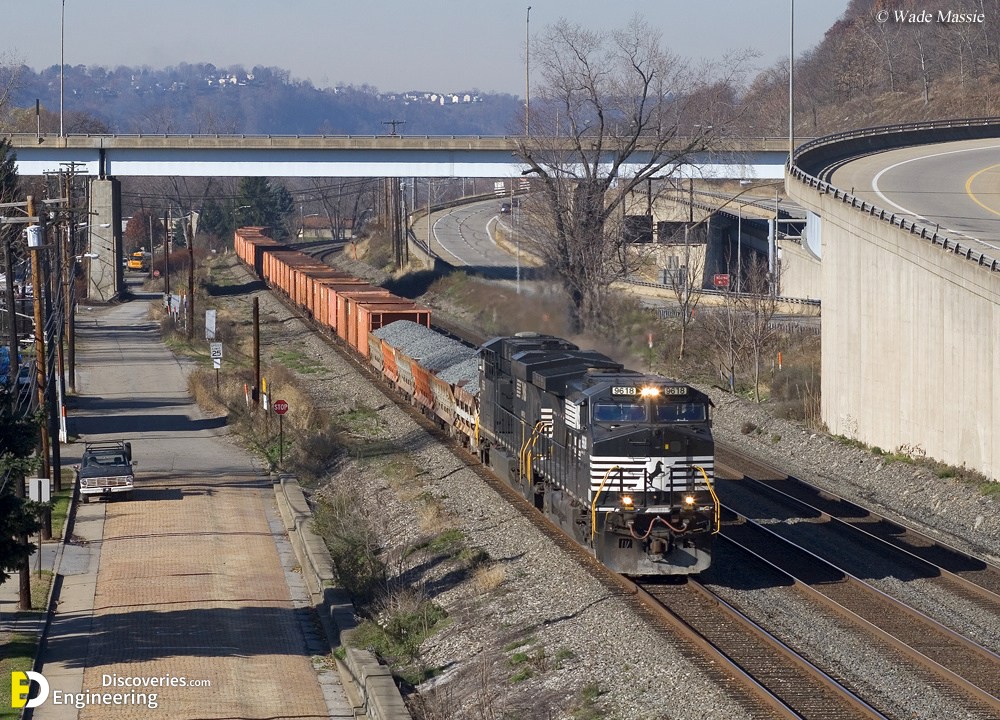
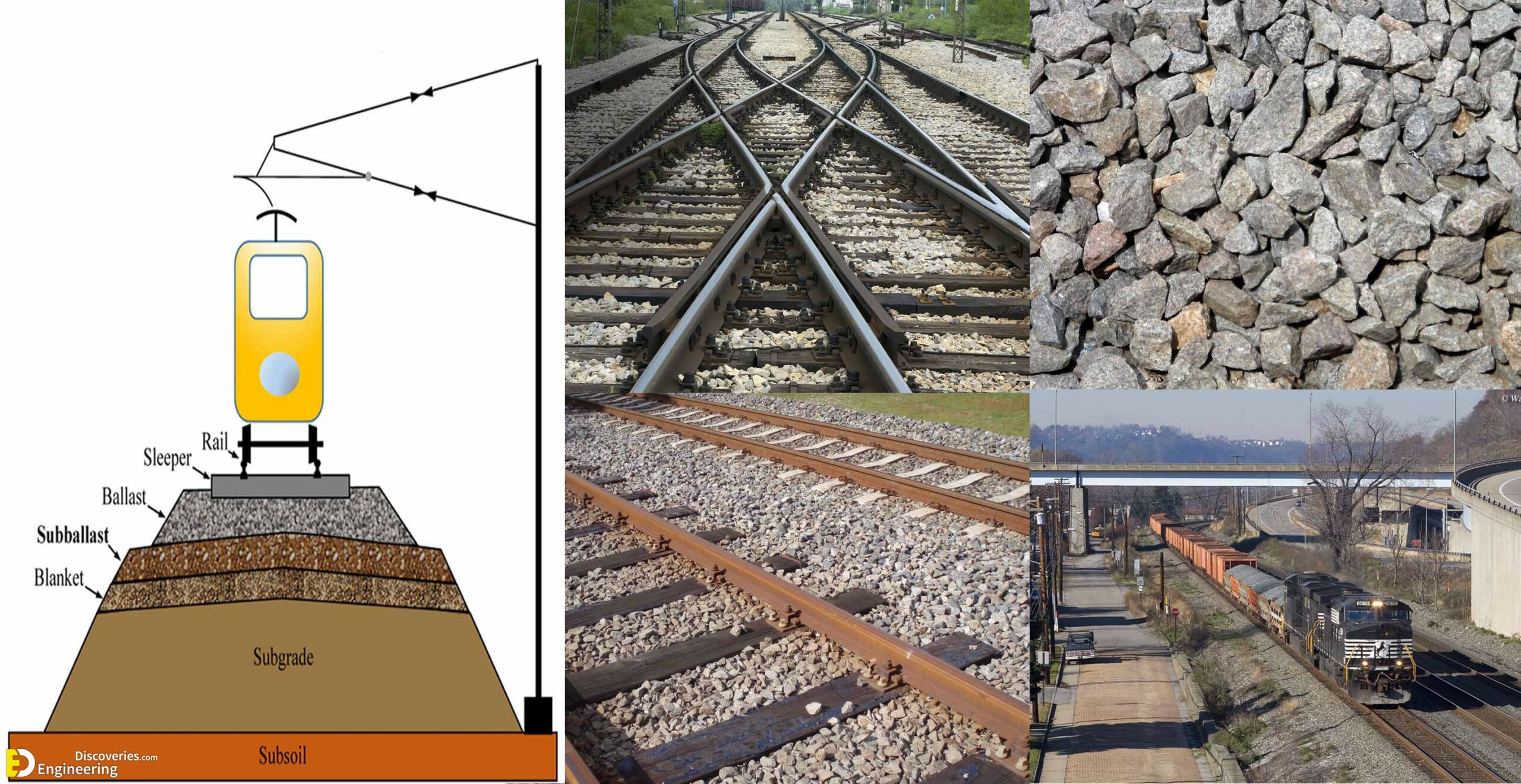
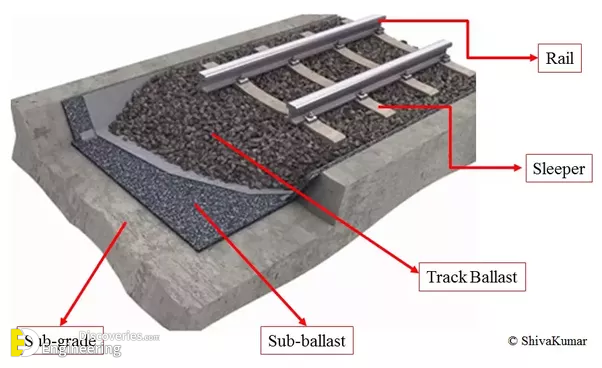
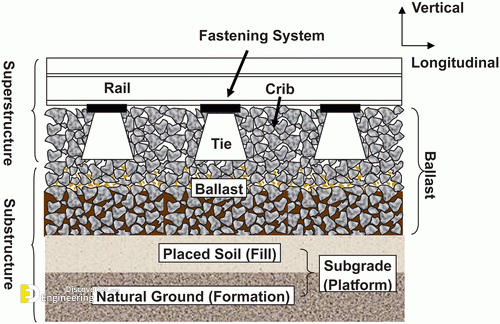
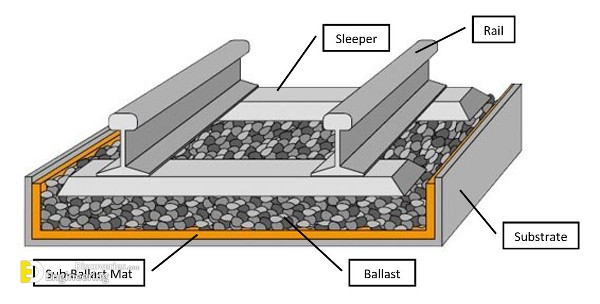
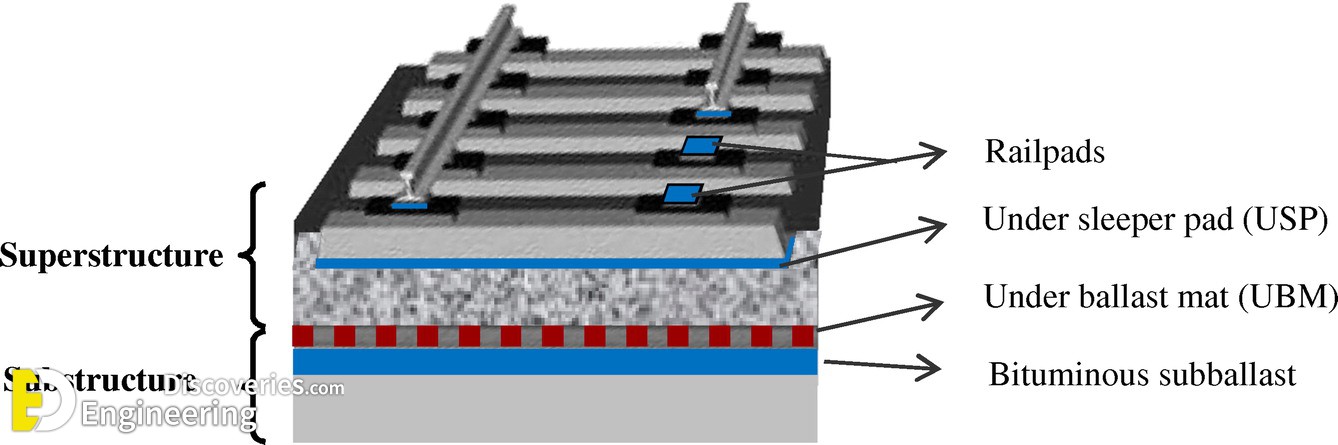
Track ballast is typically made of crushed stone, although ballast has sometimes consisted of other, less suitable materials, for example, burnt clay. The term “ballast” comes from a nautical term for the stones used to stabilize a ship. Track ballast forms the trackbed upon which railroad ties (sleepers) are laid. It is packed between, below, and around the ties. It is used to bear the load from the railroad ties, to facilitate drainage of water, and also to keep down vegetation that might interfere with the track structure.
Functions of track ballast
In fact, the track ballast serves a number of purposes. First of all, it makes sure that tracks stay in place when super-heavy trains roll by on them. It also plays an instrumental role in keeping any vegetation in check that might grow around the tracks (and make the ground beneath the tracks weaker). Another important aspect of track ballast is that it seals out any water that may be around the tracks to actually reach the tracks on a regular basis. That doesn’t mean the ballast completely insulates the tracks from water, which would be impossible, but it does facilitate water drainage around and beneath the tracks so that water doesn’t stay near the tracks and compromise the solidarity of the ground.